Logica NON-AUT
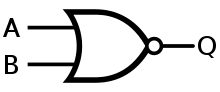
Porta NON-AUT (symbolum ANSI)
Similis portae NON-ET, porta NON-AUT est "porta universalis" quod portas NON-ET aut NON-AUT creare portas omnes alias posse significat.[1] Per exemplum, anno 1966 Apollo Guidance Computer solum ex portis NON-AUT factum est.[2].
Index
1 Porta NON
2 Porta AUT
3 Porta ET
4 Porta NON-ET
5 Porta XAUT
6 Porta NON-XAUT
7 Nexus interni
8 References
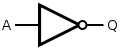
Porta NON |
Inductis portae NON-AUT iugando facta est. Quia porta NON-AUT est par portae NON post portam AUT, porta AUT deletur, et porta NON solum stat.
| Porta requisita | Constructio ex portis NON-AUT | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | |||||||||
| ||||||||||
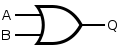
Porta AUT |
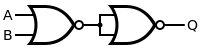
Porta AUT est porta NON-AUT ante portam NON.
| Porta requisita | Constructio ex portis NON-AUT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Porta ET |
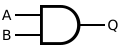
Secundum legem De Morgan, porta ET est porta NON-AUT cum uterque inductis invertis.
| Porta requisita | Constructio ex portis NON-AUT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
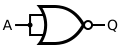
Porta NON-ET |
Porta NON-ET est porta ET ante portam NON.
| Porta requisita | Constructio ex portis NON-AUT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Porta XAUT |
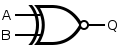
Porta XAUT aequatione logici (A ET B) NON-AUT (A NON-AUT B) sequando facta est.
| Porta requisita | Constructio ex portis NON-AUT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Porta NON-XAUT |
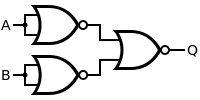
Porta NON-XAUT aequatione logici (A NON-AUT N) NON-AUT (B NON-AUT N) sequando facta est, ubi N = A NON-AUT B.
| Porta requisita | Constructio ex portis NON-AUT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Nexus interni
Logica NON-ET. Similis portae NON-AUT, portae NON-ET est quoque portae universales.
References |
↑ M. Morris Mano et Charles R. Kime (2004). Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals (3a ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 73.
↑ Hall, Eldon C. (Dec 1965). A case history of the AGC integrated logic circuits. MIT Instrumentation Laboratory